A complete guide to enterprise transformation
Last updated: March 2025
Many businesses today are undergoing radical change. The driving factor is evolving customer expectations: increasing demand for personalized products, frictionless service, and dynamic support. Improving innovation and customer service requires a massive shift in thinking. This is different than simply managing projects and delivering new capabilities.
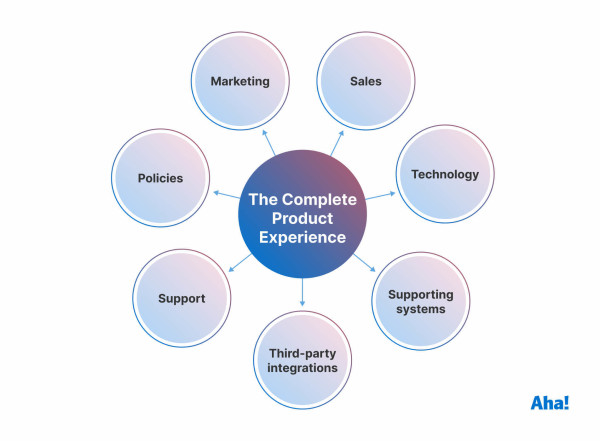
Change at this scale is called an enterprise transformation. It fundamentally shifts the entire organization's focus around delivering a Complete Product Experience (CPE). Embracing a CPE-oriented mindset requires long-term thinking about what customers really want from you beyond the product or service you provide today. It means thinking holistically about your teams, technology, and enterprise data — and how you can reshape the entire organization to better serve customers.
Drive customer-focused innovation efforts. Try Aha! software.
Enterprise-wide change is necessary to maintain growth in today's highly competitive marketplaces. To successfully transform, each business needs a unique strategy centered around the customer and the teams that get the work done. These efforts are complex and require buy-in across the organization to make a meaningful investment in the future.
This guide will help you learn the fundamentals of enterprise transformation, including the different types of transformation and guidance for getting started. Use the following links to jump ahead to a specific section:
What is enterprise transformation?
Enterprise transformation describes the different types of widespread organizational change needed to deliver better customer and employee experiences. It is also often referred to as "business transformation" (though this term can sometimes apply to smaller companies). Achieving this type of transformation requires a new approach to strategy, processes, and technology.
The concept of transformation is not new. Companies have always had to innovate and adapt to keep up with new demands. But enterprise transformation goes beyond implementing innovative ideas — it is really about rethinking how you create value at every customer touchpoint.
What are the benefits of enterprise transformation?
Enterprise transformation is primarily driven by heightened customer expectations. But it is also about business survival. Large enterprises with vast product portfolios can find it particularly hard to implement this level of change. But even though the effort to transform is monumental, so are the benefits you stand to gain:
Customer loyalty | Serve your customers better — delivering real product value that satisfies their needs. |
Strategic clarity | Set a bold vision of the future you want to achieve. This strategic direction helps teams understand how their work supports larger objectives. |
Operational efficiency | Improve responsiveness across the organization and deliver products and services faster. |
Cost reductions | Get closer to customers so you can focus resources where they matter most and strategically cut other costs. This includes choosing technology that streamlines processes and improves customer insights. |
Innovation | Reveal new customer-driven insights about the future. You can anticipate new problems to solve and develop more inventive solutions. |
Engaged teams | Bring optimism and renewed energy to your organization. Teams can see the impact of their work and understand why it matters. |
Transformation efforts are incredibly challenging and can even be emotional. Overhauling the culture and mindset of an organization means some people will respond with uncertainty and skepticism. People might wonder how they will fit into the new environment and whether changes will stick. This is why it is important to involve everyone in the transformation — with strong leadership from the CEO and executive team.
Who is involved in enterprise transformation?
Every team at your organization has a role in enterprise transformation. The most successful transformations start as a clear executive mandate with meaningful collaboration across departments. Some organizations even form innovation groups or transformation teams to lead the charge. Here is a comprehensive list of the different teams to get involved and their scope:
Leadership | Leadership sets the company vision, communicates the "why" behind enterprise transformation, and makes strategic decisions related to people, processes, and technology. This is why most enterprise transformations cannot move forward without executive sponsorship. |
Product management | Product managers sit at the intersection of design, technology, and business. The PM's role in an enterprise transformation is indispensable: reimagining the customer experience throughout the entire product lifecycle. |
IT | IT teams build and maintain the underlying technology that makes it possible for an organization to deliver its products and services. This department enables faster delivery, greater flexibility, and improved reliability. |
Marketing | Marketing teams are responsible for modernizing the entire customer journey: how the organization attracts prospective customers and communicates product value. |
Sales | Sales teams are in charge of delivering more personalized, seamless buying experiences to customers. Many teams are reshaping sales conversations to provide an expert-led, consultative approach. |
Customer support | Customer support engages with customers at key milestones when they need help or choose to upgrade, renew, or cancel. This team is integral to the transformation — responding quickly to points of friction and bringing visibility to customer feedback. |
Legal | Legal teams ensure new customer experiences and technologies meet compliance and legal requirements. This is especially important in heavily regulated industries, such as healthcare and financial services. |
Finance | Finance teams are responsible for integrating payment systems and processes to provide a smoother customer experience. They also analyze new business models to support transformation. |
HR | HR teams strengthen employee engagement in transformation efforts. They also recruit and hire new talent who will help drive organizational change. |
The role of product management in business transformation
Product managers are often in the best position to understand what customers actually want. You interview users and understand their needs. You define personas and develop product strategies. And you work with cross-functional teams to bring the new vision to life.
So it makes sense that product managers are primed to guide new customer experiences. Enterprise transformation requires strategic planning, data awareness, and customer focus — areas where strong product managers excel.
The transformation may be mandated by the executive team, but product managers are the vital link between the strategy and the tangible work that makes it happen. In this way, product managers play a leadership role in enterprise transformation by driving efforts that deliver business, customer, and product value.
Related:
Types of enterprise transformation
When you think about overhauling the way a business works, the concept of enterprise digital transformation often comes to mind first. It is all about adopting new technology and processes to modernize your business. But in fact, it is just one component of a full enterprise transformation.
There are three key strategies for achieving meaningful business transformation: applying new digital technologies, focusing on solutions, and leveraging data. Some companies focus on just one type of transformation, but many employ all of them to increase the value they deliver.
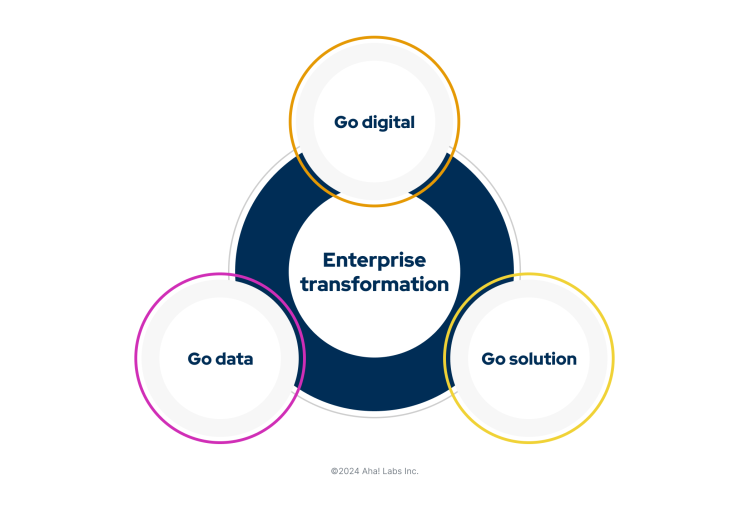
Here is a brief overview of each type of enterprise transformation, including examples:
Focus | Benefit | Impact | Example | |
Digital transformation |
|
| Allows companies to acquire, retain, and assist customers more effectively while simultaneously reducing spend | A company using on-premises software and manual processes adopts a cloud-based platform to streamline operations and improve customer service. |
Solution transformation |
|
| Enables companies to increase revenue by addressing customers' needs in a more complete way | A company provides concierge-level customer support with the product at certain pricing tiers. |
Data transformation |
|
| Keeps the entire organization focused on delivering better customer outcomes based on data | A company invests in a powerful analytics tool that allows it to convert vast amounts of data into actionable insights. |
Related:
How to get started with enterprise transformation
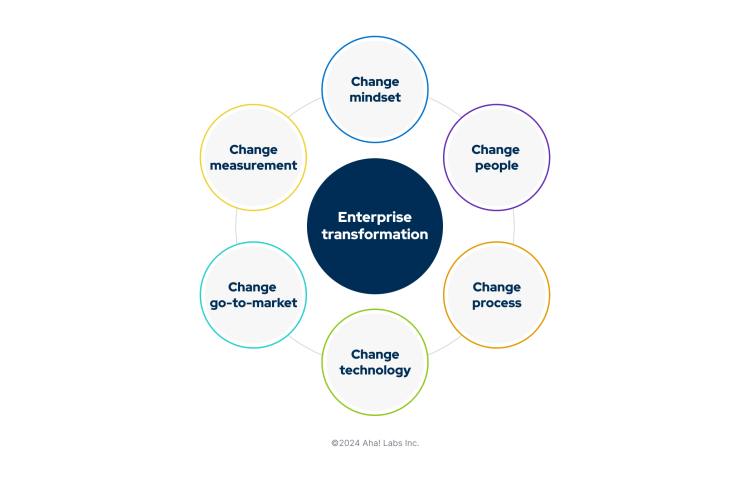
There is no quick fix when it comes to enterprise transformation — it is a years-long, ongoing process that requires serious thought and effort. Some transformations stall because the organization lacks clear strategic planning and alignment. It helps to begin with a stated set of objectives that identify where you need to improve and why. Then, as your strategy takes shape, there are six areas of change you must embrace to realize a successful transformation:
Mindset: Shift your focus to improving the customer experience. And make sure the entire organization deeply understands this path forward.
People: Identify people with the necessary skills to move the organization forward. This applies to technical skills as well as leadership and communication skills.
Process: Consider agile, lean, or DevOps initiatives to help accelerate your transformation and improve cross-functional efficiency.
Technology: Explore implementing new technologies — cloud, mobile, or AI — to deliver the experiences customers want.
Go-to-market: Rethink how you market, sell, and support your product or service to remove friction at each stage of the customer lifecycle.
Measurement: Reevaluate your current key performance indicators and choose milestones and metrics that tell a richer story about your customers.
Business transformation looks different for every company. This is because each one has different strengths to leverage and challenges it needs to address. You have to evaluate which types of transformation (digital, solution, or data) will help you achieve your objectives and how much to invest in each. The following questions can help you understand the right transformation strategy to pursue:
How satisfied are customers today?
What changes will improve their experience?
What challenges prevent the company from delivering that today?
How would investments in technology improve the experience?
What problems do customers try to solve with your products and services?
How effectively do your products and services address these needs?
What data does your company need to better understand customer behavior and preferences?
What customer outcomes do you want to achieve?
How will success be measured?
Remember: Regardless of whether a company undergoes a digital, solution, or data transformation — or all three — what matters is delivering an exceptional customer experience and setting a clear vision and strategy to get there.
Creating a business transformation roadmap
Successful enterprise transformation requires a forward-thinking and strategic mindset. Look beyond current goals to develop a strategy that anticipates customer demands a few years ahead (as well as further into the future).
You can anchor this long-term work using a business transformation roadmap, which can help guide and align all efforts throughout your transformation. Here is how to get started:
Set strategy: Define a clear vision for the future and establish measurable goals to track progress. For transformation at this scale, this work should be measured in years and be separate from the current state of your product and business. Think deeply about the customer experience you want to offer and how digital, solution, and data transformation strategies can work together.
Engage stakeholders: In the early stages, but also throughout the entire process, identify and align with stakeholders on the strategic direction your company is heading toward. Consider all relevant groups and how they connect to one another and your customers.
Celebrate milestones: Planning several years into the future can be hard to conceptualize and stay energized about — progress is often slow and hard to spot. So identify and monitor key milestones on your roadmap (like the implementation of a new digital platform). Link these major milestones to the releases, epics, and major features the team is delivering against to show incremental progress.
Customize a strategic roadmap in Aha! Roadmaps for any long-term project or cross-functional initiative.
Ultimately, all the work that goes into an enterprise transformation will help your organization become more resilient and delight your customers. To find success, stay focused on the "why" behind the changes you elect to make. Ensure that every shift ties back to this.
FAQs about enterprise transformation
Each business transformation strategy (digital, solution, or data transformation) maps to its own set of success metrics, of which there are many — from customer conversion to data availability. The metrics you choose to track depend on how you approach transformation. Be intentional and selective with which data you monitor and keep in mind that you might need to wait a year or more to determine the true impact.
We recommend using an enterprise digital transformation roadmap. This type of roadmap helps everyone stay aligned on organizational efforts both now and over the next several years. For example, a strategic roadmap in Aha! software can track progress on cross-functional initiatives within any time frame.
It is also worth exploring other frameworks to help you make consistent, strategic decisions on an ongoing basis. For example, we use The Aha! Framework to set clear goals that carry through every stage of the product development process.
There is a major misconception that transformation is all about technology. There is no doubt that technology initiatives are part of it, but this alone is not sufficient to deliver better customer experiences. Companies must leverage technology in conjunction with other strategies and shifts in mindset to satisfy customer needs.
Another major misconception is that transformation means going agile. While changing underlying processes is a necessary aspect, it should not be viewed as the primary reason for transforming. Companies must understand what their customers want before accelerating the development and delivery of new products.
Companies going through a business transformation have to rethink much of what made the company successful to start with. Here are some of the common challenges that can hinder transformation projects:
Companies must listen to customers better than ever before and gather feedback in real time to continuously improve.
Companies must plan, build, and deliver new experiences in an agile way that allows rapid iteration.
Companies must create a transparent and collaborative environment that overcomes internal silos.
A lack of technical leadership and expertise can make it difficult to respond quickly to market disruption and make the right investments.
The lack of a shared tool to bring people together contributes to confusion, misunderstandings, and oversights.
These challenges are amplified in large enterprises. Legacy processes, policies, and systems often stand in the way of change and slow down progress.